“A comparative study of four different storage solutions on graft survival in follicular unit extraction (FUE) hair transplantation”
Wilawan Damkerngsuntorn MD1, Kongkiat Laorwong, MD, FISHRS1, Ratchathorn Panchaprateep, MD, PhD, FISHRS2*
1Absolute Hair Clinic, Bangkok, Thailand
2Division of Dermatology, Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand
Conflicts of interest: None
Funding source: This is an ISHRS research grant funded in October 2022.
Abstract
Introduction: In hair transplantation surgery, the storage solution plays an important role in enhancing better graft survival. The valid comparative study of ideal storage solutions is lacking.
Objective: To compare the effect of four different storage solutions; William E media (Gibco™), chilled custom-made Dr.Kongkiat’s solution, Custodiol®HTK solution (Dr. Franz Köhler Chemie GmbH, ) and chilled normal saline, on the graft survival rate and hair thickness in FUE hair transplantation.
Methods: Four patients, with male pattern hair loss (Norwood-Hamilton class IV-VI), underwent FUE Hair transplantation. Transplanted grafts were prepared in four different storage solutions of William E media (Gibco™), chilled custom-made Dr.Kongkiat’s solution, Custodiol®HTK solution (Dr. Franz Köhler Chemie GmbH, ) and chilled normal saline. Grafts were placed in each study box designed for 30 graft/cm2 density from four different storage solutions. Digital and dermoscopy-guild photographs were obtained at baseline, month 2, month 4, month 6, month 8, month 10 and month 12. Two blinded hair restoration surgeons evaluated the grafts survival rate and hair thickness at each visit.
Results: The percent of graft survival in Dr. Kongkiat’s solution at post-op month 2 was significantly higher than William E and Custodial®HTK solution with p-value <0.05. At post-op month 4, the result showed the percent of graft survival in Dr. Kongkiat’s solution was significantly higher than the other storage solutions. There was no difference between groups at post-op month 6. The percent of graft survival in Dr. Kongkiat’s solution was significantly higher than William E media and Chilled Normal Saline with p-value <0.05 at post- op month 8, 10 and 12 but showed no difference to Custodial®HTK solution, similar to the result from hair survival rate. In terms of hair thickness, the result showed Dr. Kongkiat’s solution was significantly higher than the other solutions at post-op month 6 and month 8 with p-value <0.05. The results showed no statistically significant difference between groups at month 10 and month 12.
Conclusion: Chilled custom-made Dr.Kongkiat’s solution provides better graft survival, enhances hair thickness as well as reduces hair shedding in FUE hair transplantation.
Introduction
For decades, many new techniques were introduced to achieve a successful outcome in hair restoration surgery. Graft survival was determined by several factors including donor harvesting, graft preparation, graft storage, ischemia/reperfusion injury.(1) When hair grafts are harvested, they have to stay out of the body for many hours. Therefore, the good holding solution is key to preserve the capability and the survival rate of these grafts. The ideal holding solution should minimize cell swelling, maintain ionic balance, prevent free radicals’ formation, and provide essential substances. There are 3 main categories of storage media: (1) intravenous fluid, (2) culture media and (3) hypothermic solution.
The most commonly used storage solutions are normal saline, lactated Ringer’s solution which are inexpensive and provide acceptable outcome.(2) More expensive solutions such as Hypothermosol, Viaspan, Wisconsin Solution or Platelet Rich Plasma have claimed a better outcome. The factors that need to be considered regarding the storage solutions are ionic concentrations, pH, osmolality, and additive substances. (3)
Chilled normal saline is one of the first solutions used as a graft holding solution. The previous study showed that graft survival was a time-dependent decrease between 2 to 48 hours. The survival rate is varied from 70-100%. Therefore, chilled normal saline is suitable for the case that graft will stay out of body less than 6 hours.(4) In addition, normal saline is an extracellular ionic balance, it can cause cell swelling and damage when graft was stored at low temperatures by .(5)
Intracellular storage solutions have been used as graft storage solutions because they provide osmotic support to cells. The examples of these solutions are Custodiol®HTK, Hypothermosol, Collins, Euro Collins, Viaspan (University of Wisconsin Solution), CryoStor, Celsior, Unisol, and KPS1. Custodiol®HTK is approved as multi-organ procurement (heart, liver, kidney, pancreas, composite tissue) for perfusion and irrigation of donor organs before or immediately after being extracted from the donor. The solution is maintained in the vasculature of the organ during hypothermic storage and transport to its recipient. In hair transplantation, hypothermic solution can prevent cold injury by combat ischemia and decrease oxygen demand.
Kongkiat’s solution is custom-made solution, which is intracellular fluid with other addictive substances including, dextran, mannitol, K2HPO4, KCL, MgSO4 and Calcium gluconate, glucose, glutathione and adenosine.
Culture media is another good option for graft holding solutions. Williams E media is an extracellular holding solution that contains essential amino acids, essential vitamins, and inorganic salts, glucose and pyruvate and glutathione. Previous study showed that William E media can promote higher survival rates compared with normal saline.(6)
Until now, there is no valid comparative study of all 3 main types of storage solutions. The aim of this study is to compare the effect of four different storage solutions; William E media (Gibco™), chilled custom-made Dr.Kongkiat’s solution, Custodiol®HTK solution (Dr. Franz Köhler Chemie GmbH, ) and chilled normal saline, on the graft survival in hair transplantation.
Objectives
The objective of this study was to compare the effect of four different storage solutions; William E media (Gibco™), chilled custom-made Dr.Kongkiat’s solution, Custodiol®HTK solution (Dr. Franz Köhler Chemie GmbH, ) and chilled normal saline, on the graft survival in hair transplantation.
Study design
Methods and material
This is an ISHRS research grant funded in October 2022.
Patient Population
Four male patients between the age of 18-45 years with androgenetic alopecia (Norwood-Hamilton class IV-VI) were included in the study. Patients were excluded if they 1.) had underlying unstable medical conditions 2.) received topical medication for the hair loss within 6 months 3.) took finasteride or dutasteride or oral minoxidil within 12 months 4.) received light or laser therapy for the hair loss within 3 months 5.) received any medications that could cause hypotrichosis or hypertrichosis 6.) received any other treatments that could affect hair growth.
Study Design
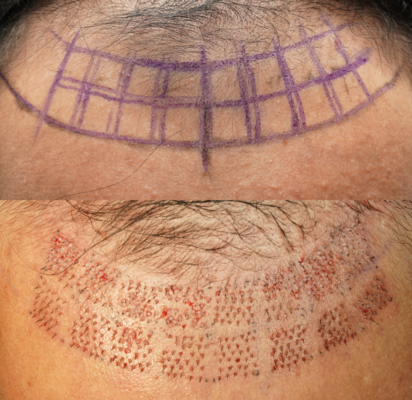
This is a pilot study. All subjects will be informed of the methodology and expected surgical results. A follow-up visit will be conducted at baseline, every 2 months until 12 months. All four patients will undergo hair transplantation using the FUE technique. Before surgery, two rows of eight separate 1×1 cm study boxes were tattooed for a total of 16 boxes depending on the area. A 1.5mm-wide bald skin area was left around each study box to facilitate hair counting. Each box was designed for 30 graft/cm2 density from four different types of storage solutions. The boxes from center outward to lateral side were for grafts prepared in four different storage solutions of William E media (Gibco™), chilled custom-made Dr.Kongkiat’s solution, Custodiol®HTK solution (Dr. Franz Köhler Chemie GmbH, ) and chilled normal saline. Moreover, the type of the storage solutions prepared for each box were also randomed in order to eliminate confounding factors caused by difference in blood supply in each scalp location.
After FUE extraction, each type of hair grafts (2-hair, 3-hair) was equally separated and stored into 4 types of storage media ((1) William E media (room temperature), (2) chilled Kongkiat’s solution, (3) chilled Custodiol solution and (4) chilled normal saline. The grafts were then placed by implanters at different times out of body: 2, 4, 6 and 8 hours. The 2-hair FU grafts were placed in the first row consisting of 8 boxes. For the second row, we placed the 2-hair FU grafts in the anterior half part of the box and the 3-hair FU grafts in the posterior half part.(Fig. 1)
Three out of four patients, the 2-hair and 3-hair FU grafts and the storage solutions were utilized according to the protocol. While the last patient, only the 2-hair FU grafts were utilized in all boxes because the patients did not have enough 3-hair grafts.
Figure 1. Recipient site – two rows of eight 1×1 cm study boxes with 1.5mm-wide bald skin area was left around each study box to facilitate hair counting. Each box was designed for 30 graft/cm2 density from four different type of storage solutions.
Clinical evaluation
Clinical evaluation will be assessed at pretreatment time (Week 0) and each following visit at month 2, month 4, month 6, month 8, month 10 and month 12. Hair survival rate will be evaluated using (i) terminal and total hair count, (ii) standardized global photographs, (iii) evaluation of the adverse events.
Total hair count and hair thickness
The total hair count on each box will be performed using dermoscopy-guided at every visit. The fine vellus hair was excluded. Hair counts were performed by two hair restoration surgeons. The hair thickness was evaluated at month 6, month 8, month 10 and month 12 using the digital dermoscope FotoFinder, Leviacam device
Global photographic assessment
Global photographs were taken with a digital camera at baseline, month 2, month 4, month 6, month 8, month 10 and month 12 to evaluate hair growth.
Evaluation of the adverse events
Statistical analysis
Data were presented as mean and standard deviation (SD). Comparison of grafts survival rate, hair survival rate and hair thickness was used in a linear mixed-effect model. All P-values reported are two-sided. Statistical significance was defined as P<0.05. Stata version 18.0 (Stata Corp., College Station, Texas), was used for analysis.
Results
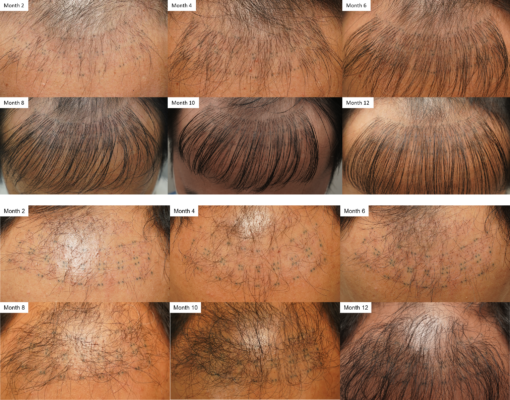
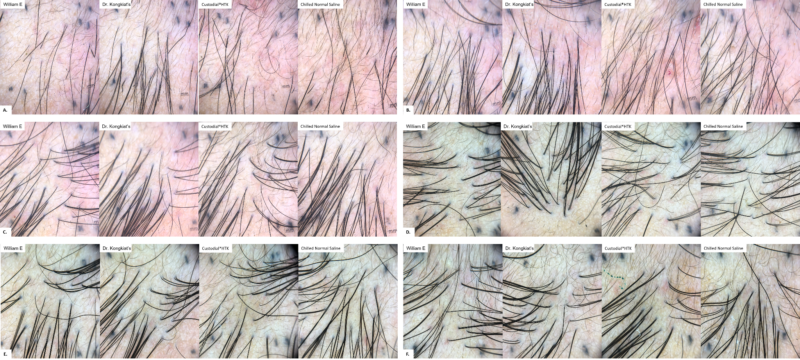
All four subjects were Thai males, ages 28,38,55 and 56 years old, with male pattern hair loss (Norwood-Hamilton class IV-VI). The total number of grafts transplanted in each study box was 30 graft/cm2 density. In three out of four patients were transplanted with 2-hairs for 90 grafts per storage media and 3-hairs for 30 grafts per storage media, total 120 grafts per media. One patient was transplanted with only 2-hairs for 120 grafts per storage media. All patients completed a 12-months follow-up period. (Fig. 2,3)
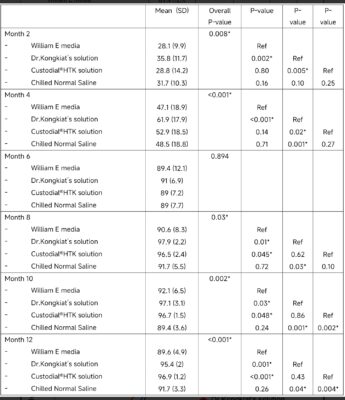
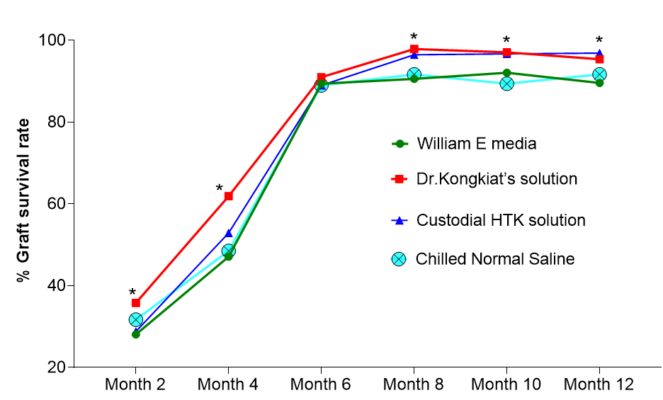
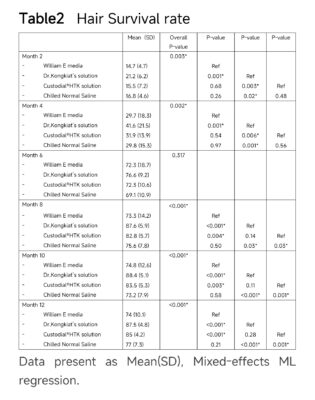
At post-op month 2 , The multilevel mixed-effects linear regression showed Dr. Kongkiat’s solution had a mean(± SD) 35.8 +/- 11.7 compare to William E media with a mean(± SD) 28.1 +/- 9.9, Custodial®HTK solution with a mean(± SD) 28.8 +/- 14.2 and Chilled Normal Saline with a mean(± SD) 31.7 +/- 10.3. The percent of graft survival in Dr. Kongkiat’s solution at post-op month 2 was significantly higher than William E and Custodial®HTK solution with p-value <0.05 (Table 1, Fig. 4). But the result showed no difference between Dr. Kongkiat’s solution and Chilled Normal Saline. Since grafts can contain varying numbers of hairs ranging from 1 to 3, hair yield from transplanted grafts provided more relevant outcome parameters than graft survival. In terms of hair survival rates, the result showed Dr. Kongkiat’s solution was significantly higher than Chilled Normal Saline with p-value < 0.05. (Table 2, Fig. 5)
At post-op month 4, the result showed the percent of graft survival in Dr. Kongkiat’s solution was significantly higher than the other storage solutions. The results also correlate with hair survival rate. Dr. Kongkiat’s solution had a mean(± SD) 61.9 +/- 17.9 compare to William E media with a mean(± SD) 47.1 +/- 18.9, Custodial®HTK solution with a mean(± SD) 52.9 +/- 18.5 and Chilled Normal Saline with a mean(± SD) 48.5 +/- 18.8 with p-value <0.05.(Table 1, Fig. 4)
At post-op month 6, the percent of graft survival in Dr. Kongkiat’s solution was higher than the other solution but showed no statistically significant difference between groups together with hair survival rate (Table 2, Fig. 5). Dr. Kongkiat’s solution had a mean(± SD) 91 +/- 6.9 compare to William E media with a mean(± SD) 89.4 +/- 12.1, Custodial®HTK solution with a mean(± SD) 89 +/- 7.2 and Chilled Normal Saline with a mean(± SD) 89 +/- 7.7. (Table 1, Fig. 4)
At post-op month 8, Dr. Kongkiat’s solution had a mean(± SD) 97.9 +/- 2.2 compare to William E media with a mean(± SD) 90.6 +/- 8.3, Custodial®HTK solution with a mean(± SD) 96.5 +/- 2.4 and Chilled Normal Saline with a mean(± SD) 91.7 +/- 5.5. (Table 1, Fig. 4)
At post-op month 10, Dr. Kongkiat’s solution had a mean(± SD) 97.1 +/- 3.1 compare to William E media with a mean(± SD) 92.1 +/- 6.5, Custodial®HTK solution with a mean(± SD) 96.7 +/- 1.5 and Chilled Normal Saline with a mean(± SD) 89.4 +/- 3.6. (Table 1, Fig. 4)
At the 12-month follow-up, mean(± SD) percent graft survival was 95.4 +/- 2 in Dr. Kongkiat’s solution, 89.6 +/- 4.9 in William E media, 96.9 +/- 1.2 in Custodial®HTK solution and 91.7 +/- 3.3 in Chilled Normal Saline. (Table 1, Fig. 4)
The percent of graft survival in Dr. Kongkiat’s solution was significantly higher than William E media and Chilled Normal Saline with p-value <0.05 at post- op month 8, 10 and 12 but showed no difference to Custodial®HTK solution, similar to the result from hair survival rate. Interestingly, there showed no difference between William E media and Chilled Normal Saline. (Table 1, Fig. 4)
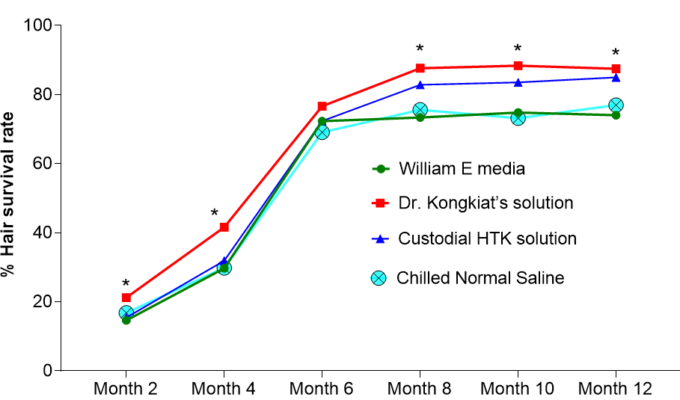
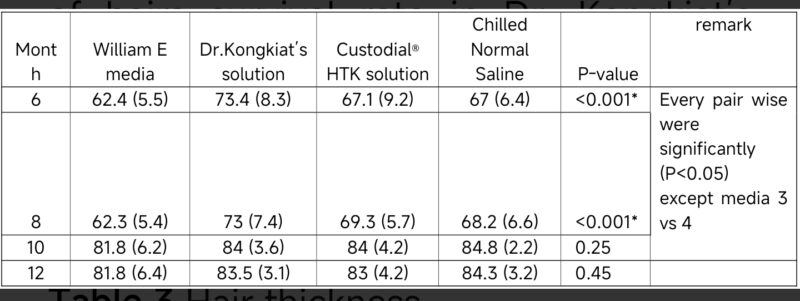
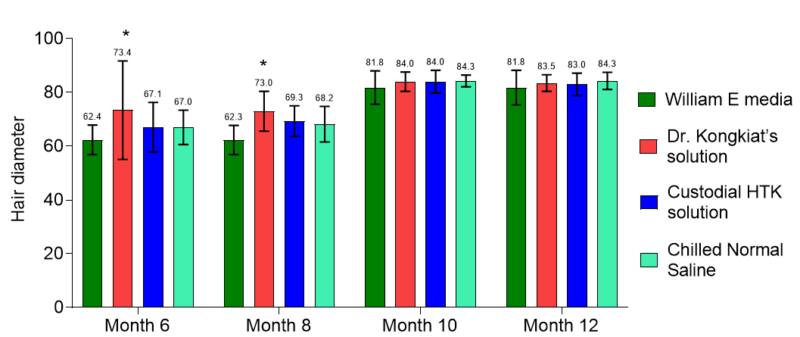
In terms of hair thickness, the result showed Dr. Kongkiat’s solution was significantly higher than the other solutions at post-op month 6 and month 8 with p-value <0.05. The results showed no statistically significant difference between groups at month 10 and month 12. Moreover, there is no statistically significant difference between Custodial®HTK and Chilled Normal Saline at post-op months 6 and 8. (Table 3,Fig. 6)
At the 12-month follow-up, mean(± SD) hair thickness was 83.5 +/- 3.1 in Dr. Kongkiat’s solution, 81.8 +/- 6.4 in William E media, 83 +/- 4.2 in Custodial®HTK solution and 84.3 +/- 3.2 in Chilled Normal Saline. (Table 3,Fig. 6)
No adverse event was observed in those subjects.
Figure 2. Photographs of post operative at Month 2, Month 4, Month 6, Month 8, Month 10 and Month 12
Figure 3. Dermoscopy-guild photographs evaluated graft survival rate and hair yield from transplanted grafts at post post operative at Month 2 (A.), Month 4(B.), Month 6(C.), Month 8(D.), Month 10(E.) and Month 12(F.) compare between storage media.
Table1 Graft Survival rate
Data present as Mean(SD), Mixed-effects ML regression.
Figure 4. Graft Survival rate – the percent of grafts survival rate in Dr. Kongkiat’s solution was higher than the others at post-op month 2, 4, 8, 10 and 12
Table2 Hair Survival rate
Figure 5. Hair Survival rate – the percent of hairs survival rate in Dr. Kongkiat’s solution was higher than the others at post-op month 2, month 4, month 8, month 10 and month 12.
Table 3 Hair thickness
Data present as Mean(SD), Mixed-effects ML regression.
Figure6. Hair thickness among media – the result showed Dr. Kongkiat’s solution was significantly higher than the other solutions at post-op month 6 and month 8 with p-value <0.05.
Discussion
One of the most important roles of the graft storage solution is to provide a better graft survival rate in hair transplantation surgery. The ideal storage solutions should provide the graft protection from reperfusion injury, free radical formation, ionic imbalance and alteration in osmolality created by the ischemic phase. Certain research suggests that economical options like normal saline or Ringer’s Lactate may be adequate, whereas others argue that pricier alternatives such as Hypothermosol, Viaspan, Wisconsin Solution, or Platelet Rich Plasma offer superior benefits. In recent times, some individuals have contemplated incorporating antioxidants, ATP, and oxygen into their graft storage solutions.
Nevertheless, there are no ideal storage solutions for hair restoration surgery based on current available studies. This study is to compare the efficacy of four different solution; William E media (Gibco™), chilled custom-made Dr.Kongkiat’s solution, Custodiol®HTK solution (Dr. Franz Köhler Chemie GmbH, ) and chilled normal saline on the graft survival in hair transplantation.
Intracellular storage s