### Understanding FUE Donor Harvesting: Techniques and Innovations
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) has revolutionized the field of hair transplantation, offering a minimally invasive and highly effective solution for hair restoration. One of the critical components of a successful FUE procedure is the donor harvesting technique. Here, we explore the key concepts and innovative strategies employed in FUE donor harvesting, focusing on terms like cherry picking, no kissing excision, equally skipping, ear-to-ear distribution, and the use of a decent size of punch.
#### Cherry Picking
Cherry picking in FUE donor harvesting refers to the selective extraction of follicular units. This technique involves carefully choosing the healthiest and most robust hair follicles from the donor area to ensure optimal growth and aesthetic results. By selecting the best follicles, surgeons can enhance the overall quality of the transplanted hair, leading to more natural-looking outcomes. This method requires a keen eye and experience to identify and extract the most suitable grafts while maintaining the integrity of the donor site.
#### No Kissing Excision
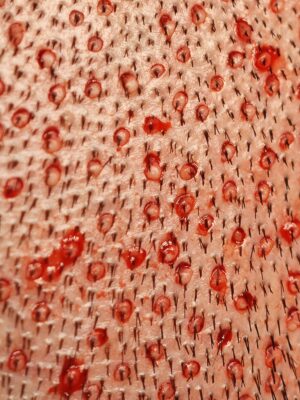
No kissing excision is a technique aimed at preventing the adjacent extraction of follicular units, which can compromise the donor area’s appearance and health. By ensuring that no two extracted grafts are directly next to each other, this method minimizes the risk of over-harvesting and ensures a more uniform and aesthetically pleasing donor area. This approach also helps in maintaining the donor site’s density, reducing the risk of noticeable scarring and allowing for potential future procedures if needed.
#### Equally Skipping
Equally skipping involves the strategic spacing of follicular unit extractions across the donor area. By skipping equal distances between each harvested graft, surgeons can avoid creating noticeable patterns or thinning in the donor site. This method ensures an even distribution of extractions, contributing to a more natural and undetectable appearance post-procedure. Equally skipping is crucial for preserving the donor area’s aesthetics and functionality, especially in patients with limited donor hair.
#### Ear-to-Ear Distribution
Ear-to-ear distribution is a harvesting technique that involves extracting follicular units from the entire donor region, spanning from one ear to the other. This comprehensive approach ensures that the extractions are evenly spread across the donor area, reducing the risk of localized thinning and scarring. By utilizing the full extent of the donor zone, surgeons can maintain a balanced and uniform appearance, making the procedure less noticeable and more aesthetically pleasing.
#### Decent Size of Punch
The size of the punch used in FUE donor harvesting is a critical factor that influences the success and appearance of the procedure. A decent size of punch, typically ranging from 0.8mm to 1.0mm, is chosen to strike a balance between minimizing scarring and ensuring efficient extraction of follicular units. A well-selected punch size allows for the precise removal of grafts with minimal trauma to the surrounding tissue, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of noticeable scarring.
### Conclusion
FUE donor harvesting has advanced significantly with the development of refined techniques such as cherry picking, no kissing excision, equally skipping, ear-to-ear distribution, and the use of a decent size of punch. These methods collectively enhance the quality of hair transplants, ensuring natural-looking results and preserving the integrity of the donor area. As technology and expertise in hair transplantation continue to evolve, these innovative strategies will remain essential in achieving optimal outcomes for patients seeking hair restoration.
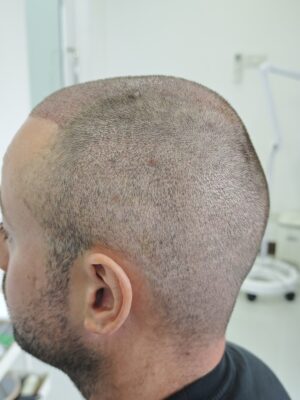
Before
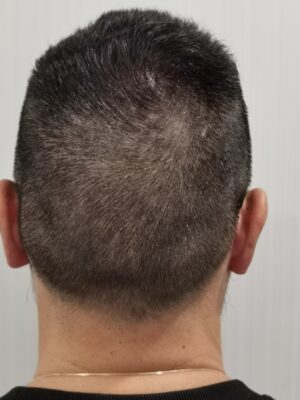
After 4000 grafts extraction